You probably don’t give much thought to earwax accumulation unless you’re in the process of clearing it out. Still, it’s essential to have an understanding of its purpose and how it develops.
What causes the accumulation of earwax?
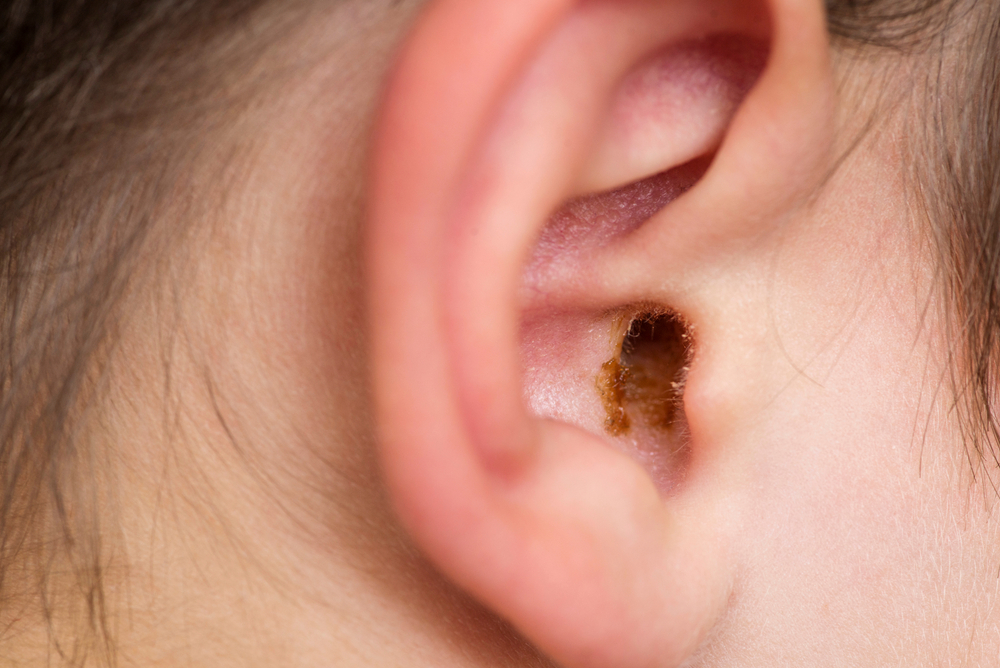
Earwax, technically called cerumen, is a thick blend of debris, hair, skin particles, sweat, and ceruminous gland secretions. This earwax presents with a waxy texture and can exhibit shades of orange, yellow, gray, or brown.
While the production amount of earwax differs from person to person, adults usually produce less earwax than children. Kids also typically have softer earwax that’s lighter in color than adults.
Earwax goes by the outer ear canal naturally, ultimately reaching the ear opening, where it either self-expels or gets washed out when you bathe.
Why do we need earwax?
Earwax serves several critical functions, such as:
- Helping counter ear infections.
- Acting as a protective barrier against external irritants like dirt, dust, and other foreign particles before they infiltrate deeper into the ear.
- Safeguarding and moisturizing the skin lining the ear canal, thereby preventing dryness and itchiness.
Obstructions caused by earwax
Impacted earwax is a prevalent issue, but it’s typically the only time you need to worry about it. Impacted earwax can be the result of narrow or abnormally shaped ear canals impeding the natural movement of earwax toward the ear’s opening.
Poor ear hygiene practices, like using cotton swabs or bobby pins, can inadvertently force wax deeper into the ear canal.
People wrestling with hearing loss who make use of earplugs or hearing aids are also predisposed to experiencing ear canal obstructions.
How is hearing affected by too much earwax?
The presence of earwax blockages might yield slight discomfort and impact auditory health.
Additionally, significant buildup of earwax can induce tinnitus, a feeling of ringing in the ears.
Untreated earwax obstructions might escalate into middle ear infections, perforated eardrums, or enduring hearing impairment due to acoustic trauma.
Dealing with impacted earwax
Should you suspect an earwax blockage, consulting us promptly is essential. You might be advised to use over-the-counter products like a bulb syringe or earwax softening drops to clean the wax out, depending on the extent of the obstruction.
Contact us right away if you need some assistance with an earwax blockage.
